About Manufacturing Plans | ||
| ||
Before Creating a Manufacturing Plan
Before a Manufacturing Planner can create a manufacturing plan for a product revision, certain steps must be completed.
-
The model associated with the product revision must have one or more master features defined. Each master feature must have managed feature or product revisions.
Master features are used by System Engineers and Product Managers to represent a technical capability a product will be designed to deliver. Master features are not components in the product structure and instead, are holders that manage the change evolution of the feature revisions that represent the technical capability. Master features are created by System Engineers at the model level and are directly connected to the model. Master features are of type Master Feature which is its own type and not a subtype of type Feature.
-
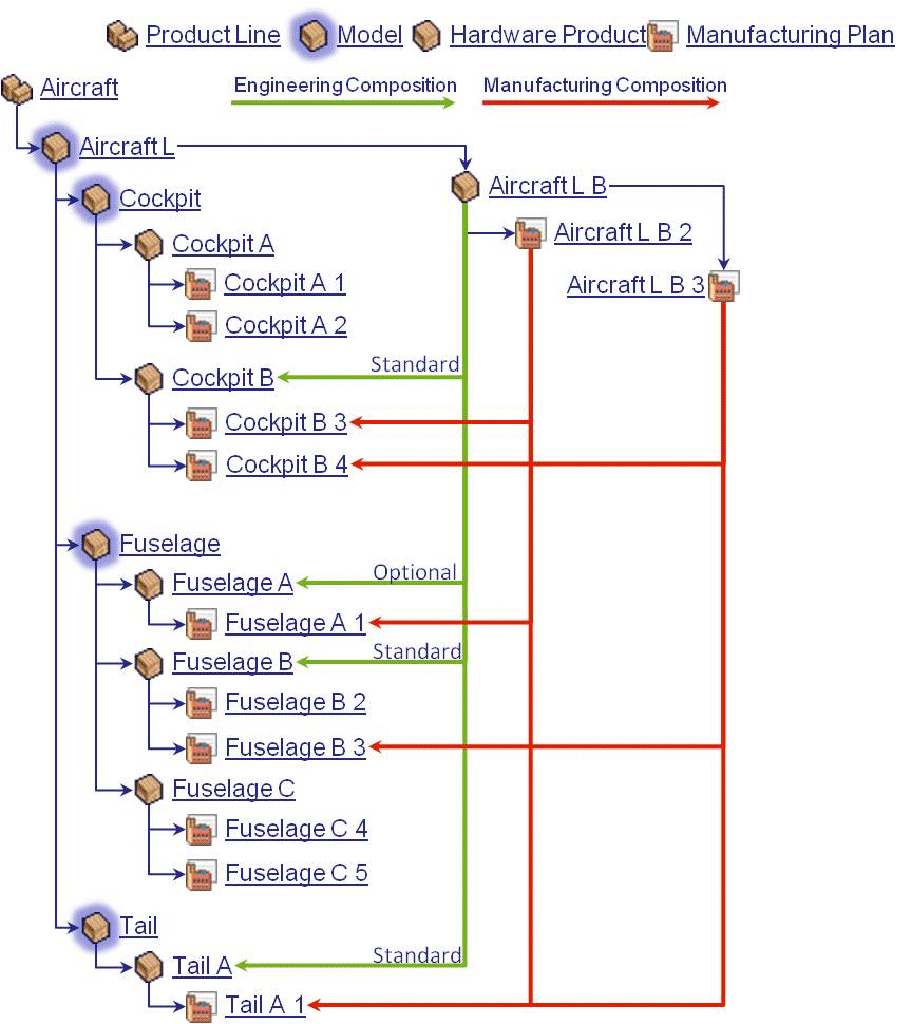
One or more
manufacturing plans must be defined for each logical feature in the product's logical feature structure.
The manufacturing plan for a logical feature is a low-level plan or step in the high level plan for the product revision. This low-level plan describes how to put or assemble components together during manufacturing for the specific engineering specification or logical feature. This plan also describes the tools to use and has resource and timing constraints.
- The product revision must be created using the design effectivity matrix from the Product Revisions page for the context model in ENOVIA Variant Configuration Central. The design effectivity matrix is used to define the product revision's logical feature structure based on the master composition defined for the context model. The master composition is a grouping of models and master features that represent components that need to be part of the different product revisions under the model. The master composition essentially defines the choices that are available for each product revision. For details, see "Creating an Effectivity Matrix" in the Variant Configuration Central User's Guide.
- A long cycle time may be necessary to produce a logical feature or product (and consequently a complete product). The program may decide to reassign a planned or launched unit to another engineering definition as the design is changed. This may lead manufacturing to "retrofit" a logical feature or product so that it ultimately conforms to the targeted engineering definition. Having the ability to capture and describe a retrofit intent at the governance level is key to being able to plan and track such a situation. It also enables proper configuration of all product planning activities.
![]()
Manufacturing Intent
The Manufacturing Plan Breakdown edition is more or less constrained based on whether the manufacturing intent is "regular" or "retrofit":
- A manufacturing intent of "regular" means that the Manufacturing Plan Breakdown should comply with its related Engineering definition.
- A manufacturing intent of "retrofit" means that the Manufacturing Plan Breakdown does not necessarily need to comply with its Engineering definition.
![]()
Manufacturing Plan Master
When the first manufacturing plan is created for a product or logical feature, a Manufacturing Plan Master is also created and associated with the manufacturing plan. The manufacturing plan master is connected to the parent object of the product or logical feature revision series. The parent object for a product revision series is the associated Model and the parent object for a logical feature revision series is the associated Master Feature.
A Manufacturing Plan Master allows you to maintain the evolution of a manufacturing plan across a product or logical feature revision series. For example, when a manufacturing plan is created for a product revision, it is maintained as a revision of the manufacturing plan defined for the previous product revision under the context model. Each manufacturing plan created for a product revision under that context model is connected to the same manufacturing plan master.
Manufacturing plans cannot be created for a product or logical feature revisions after a manufacturing plan is created for a higher revision. For example, if there are three product revisions under a model, you can only create a manufacturing plan for the latest revision. The Create action will be disabled for the earlier revisions regardless of them having a manufacturing plan defined.
The naming convention for manufacturing plan masters is <PREFIX PATTERN><MODEL/MASTER FEATURE NAME>. The prefix pattern is read from the application properties file and has a default value of MP-.
![]()
Manufacturing Plan Policy
Manufacturing plan objects are of type Manufacturing Plan and governed by the Manufacturing Plan policy.
The default Manufacturing Plan policy lifecycle has two states: Preliminary and Released. For details on this lifecycle, see "Manufacturing Plan Lifecycle" in the Application Exchange Framework Help.