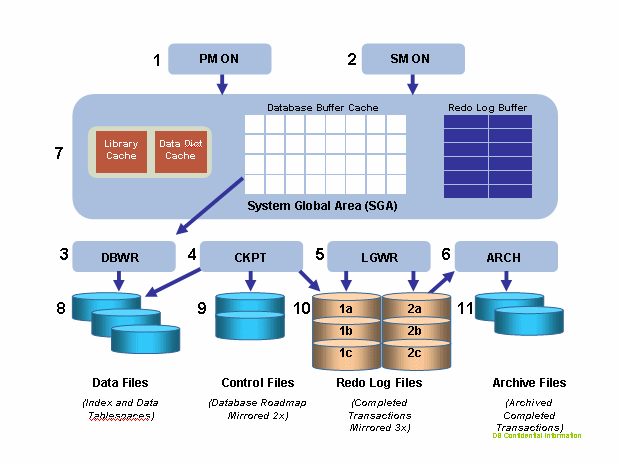
Disk Layout Suggestions | ||
| ||
There are three ways to look at disk layout:
- Method #1: Multiple disks, multiple disk spindles
- Method #2: Multiple disks plus Raid Arrays
- Method #3: Advanced Storage devices using large scale write buffer caches
There are multiple Oracle processes that involve writing to disk:
- DBWR--writes data from the database buffer cache to the database datafiles; that is, to the ENOVIA Live Collaboration user datafile, to the data, and index datafiles.
- DBWR--will also write rollback data to the rollback datafile, also any temp/system datafile updates.
- LGWR--writes data from the log buffer to the redo log files (possibly mirrored).
- ARCH--if enabled, will copy off redo logs at redo log switch time only.
In addition, ENOVIA Live Collaboration may involve a write to local disk for FTP/NFS file transfer as part of file checkin/checkout transactions, if stores are locally configured.
So, for a fully-used production system, as transaction updates are
made continuously by a large pool of people, or during dataload, parallel
writes to disk for vault datafile, index datafile, redo log and rollback
datafile occurs. Temp datafile updates may also occur. The diagram below
shows all possible write transactions.