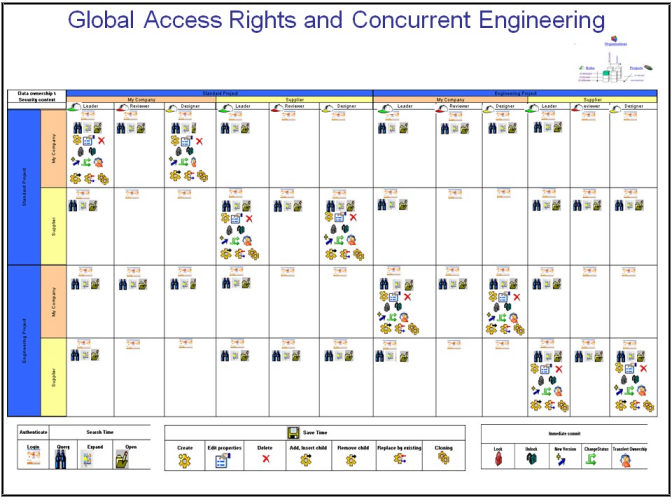
When Are Security Checks Applied? | ||
| ||
and on both the server side and the client side.
Security Checks on the Server Side
Policies and rules on the ENOVIA V6 server side manage access rights:
- access rights are used to manage access to PLM objects:
Create, Read, Show, Modify, ChangeOwner, CheckIn, Delete, FromConnect, ToConnect, FromDisconnect, ToDisconnect, Revise, Promote, ChangeName, Lock, Unlock
- there are thirty-two available access rights, and the list is not extendable
Security is defined within the data integrity and lifecycle scope:
- the lifecycle is defined on PLM references
- access rights are defined on PLM references, connections and ports via a policy on types
- access rights can also be defined on PLM instances via a rule on relationships
- access rights are tied to the lifecycle to manage the integrity and consistency
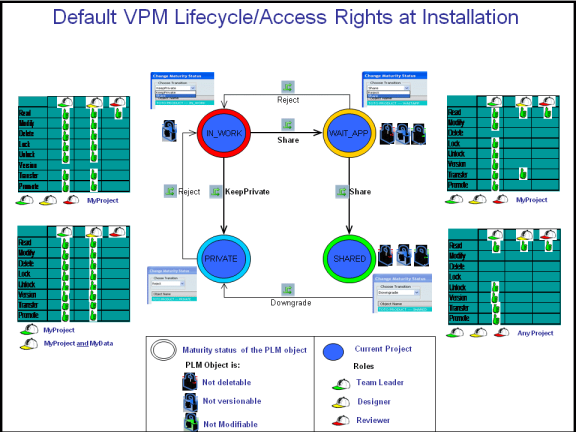
Default VPM Lifecycle and Access Rights at Installation
The VPLM_SMB policy governs all PLM reference types.
The following illustration describes in one picture how this policy governs the lifecycle and access rights for all roles, for all PLM reference types, for the operations:
- Read
- Modify
- Delete
- Lock
- Unlock
- Version
- Transfer Ownership
- Promote.
Note: The names of each lifecycle status (IN_WORK, PRIVATE, SHARED, WAIT-APP) are not translated: they are in English only.
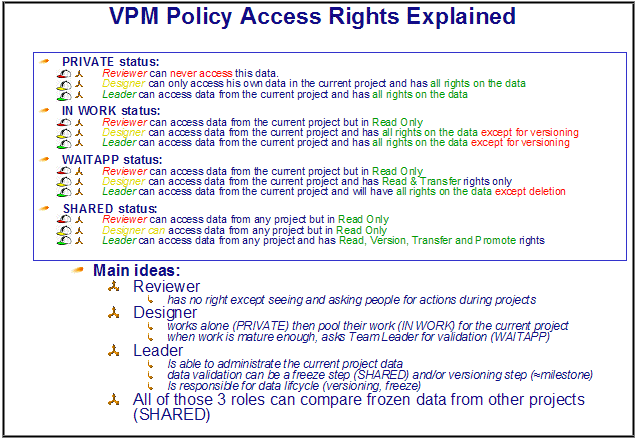
Explanation of the Access Rights Granted by the Principal Policy
The following figure explains which type of access rights the principal policy grants to the different roles for each phase in the lifecycle:
Then, the following table lists the VPLM V6 operations and commands concerned by the principal security policy, classified in three categories:
- search commands
- save commands
- and short transactions (immediate commit)
and maps the operations and commands to the appropriate access rights determined by the policy and rule(s):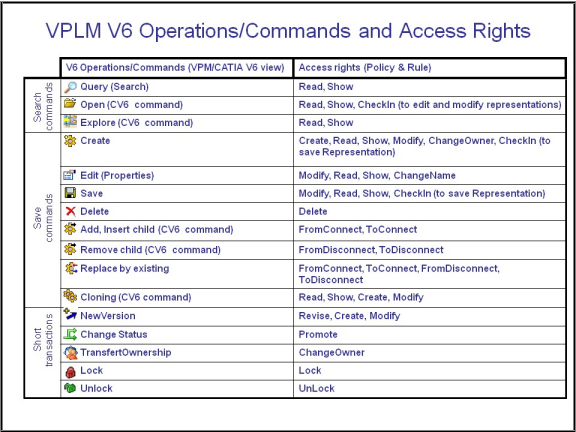
![]()
Security Checks on the Client Side
User commands
A command is an administration object that can be used by an application to comprise a menu.
It is secured through a basic access mechanism that grants authorization to one or more P&O objects (a P&O object being a person, role, organization, project, security context).
A command must be granted. It will be computed at login time and checked for client sessions.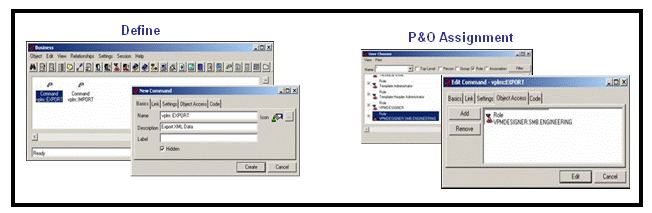
Masks
Security masks specify and secure the access authorizations to PLM objects and their attributes.
A mask can be defined succinctly as a set of access control information for objects and attributes.
A mask may be seen as default for any P&O or may be customized via the P&O software. An Attribute access control is defined per operation (Create, Query, Browse, Edit, ..)
Masks are set up by the PLM administrator and assigned to P&O objects if needed.
Default Rule Provided at Installation
A default rule is provided at installation.
The rule is:
VPLM_SMB_INSTANCE
This rule contains several filters (one filter for each security context and other general-purpose filters) and can be viewed, for example, using MQL or by using the ENOVIA V6 Business application by searching for rules.
Filters are provided for the principal security contexts and define the security for access to instances for all states following the policy concept explanation outlined in "Implementing Security on VPLM Application Commands".
Note: Rule VPLM_SMB_DocumentCheck should be modified when new roles are created. For instance, if role VPLMManager is created, the rule must be modified as follows:
modify rule "VPLM_SMB_DocumentCheck" user "VPLM_SMB_DocumentCheck" all;