Security Mask Concepts | ||
| ||
Note: The application server must be restarted after modifying masks.
What is Object Access Control?
Object access control, as the name suggests, is used to control access to PLM objects and their corresponding attributes to determine how end users can manipulate them using the graphic user interface of a PLM application.
When manipulating PLM objects, the main generic kinds of access that you can provide to these objects are:
- create: a creation dialog box containing different attribute fields lets you create the object
- query: a generic query dialog box lets you perform queries on objects using different object attributes as query criteria
- browse: once you have run the query, a list with the query results is displayed, with the information filtered by attribute columns so that you can browse query results
- edit: after selecting an object you created or loaded, you can then edit the object's properties using the appropriate attribute fields.
These different operations are performed in views.
Furthermore, object access control provides the possibility in these views to specify whether an object is modifiable or not.
![]()
What Is a Security Mask?
Object access control is implemented using security masks. Security masks specify and secure the access authorizations to PLM objects and their attributes.
A mask can be defined succinctly as a set of access control information (ACI) for entities and attributes. Masks are set up by the PLM administrator, and are associated to security contexts, roles, projects or organizations.
The purpose of a mask is to filter the user interface of PLM applications for either customization or security reasons to provide finely tuned object access control. A mask controls which object attributes are visible in create, query, browse, and edit views, and which are modifiable or not. Masks also let you customize other attribute characteristics such as default values and authorized or help values.
After installation the only existing & deployed mask is the mask named DEFAULT.
You can also create your own masks. The default mask is suitable for the majority of security purposes. If this mask does not meet your object access security needs, we recommend that you create other masks for this purpose.
The default mask is not associated with any particular security context.
An entity is a type of PLM object. You control access to the PLM object's attributes via the use of a mask. Masks reference entities. Entities not defined in a mask are not masked: this means that all their attributes are visible and accessible, according to IP Protection rules.
This DEFAULT mask references a list of entities (PLM objects) that are controlled by the mask. It is always active: it cannot be replaced by another mask, and MUST NOT be deleted. Entities not referenced by the default mask are not controlled by this mask but may be controlled by a customer-defined mask.
Nothing prevents you physically from modifying or customizing the default mask. However, we recommend that you do not. If you do, and then install, for example, a higher hot fix level, the default mask will be overwritten and you will lose your changes.
To prevent from any issue, we recommend associating mask information to each entity.
There are 7 pre-defined access operations on attributes:
- Create
- Query
- EZQuery
- Read
- Write
- Tree
- List.
Note: "List" is not currently used and is reserved for future use.
![]()
Where Are Masks Stored?
Security mask definitions on entities and attributes are not stored in the ENOVIA V6 database, but are stored as files with the extension .SecurityMask located in the ENOVIA V6 server installation filetree.
A .SecurityMask file is generated by compiling source files (whose extension is simply .mask).
Mask files are human-readable text files that contain the mask definitions on entities and attributes manipulated by the different PLM applications. They use a proprietary syntax also described later.
If you decide to generate your own masks, the following tools are provided:
- VPLMPosMaskGenerator: generates a .mask file from metadata files and inherited mask files
- VPLMPosMaskCompiler: compiles mask files and generate a .SecurityMask file.
![]()
Filepath Nomenclature
For the purposes of this section, the variable:
<ENOVIAPlatformServer_WEB-INF>
is:
install_folder\server\Apps\VPMMultiDiscipline\V6R2013\WebAppRoot\WebAppName\WEB-INF\
For example:
<ENOVIAPlatformServer_WEB-INF>\classes\vplm\mask
could be (depending on your installation):
E:\enoviav6r2013\server\Apps\VPMMultiDiscipline\V6R2013\WebAppRoot\WebAppName\WEB-INF\classes\vplm\mask
![]()
Static and Dynamic Aspects Involving Masks
The ENOVIA V6 PLM model comprises two important aspects:
- a Static model
- a Dynamic Model.
The static model describes entities, attributes and relationships. Data structures are defined by metadata files, and are complemented by public mask definitions. Masks definitions:
- set default values
- set authorized values
- and can override structure characteristics (mandatory).
Note: Relationships are currently expressed through instantiation, and ports and connections.
So we can say that a security mask extends the static model (mainly expressed by metadata), by adding or overriding attribute definitions.
The dynamic model describes behavioral aspects. We can say that a security mask manages entity attributes usage (the attribute is visible or not) and access (the attribute is modifiable or not).
The dynamic model also features a Policy model, where each policy implements:
- a lifecycle specification, with states and branches
- security specifications with object accesses, depending on states
- miscellaneous characteristics such as Store, Version sequence, formats, etc.
![]()
More About the PLM Model and Masks
The following diagram describes the inheritance tree of a given customized entity MyCustoProductRef (defined in MYCUSTO metadata file) up to the common base entity PLMEntity (defined in PLMABSTRACT metadata file) going through the modeller (here PRODUCT) and PLMCORE layers:
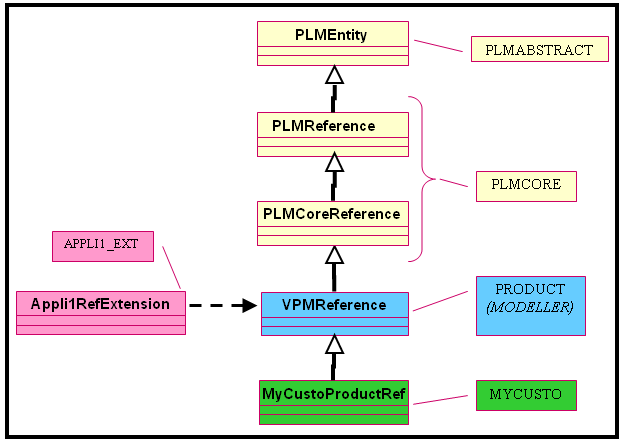
Security masks can be defined for the entities and attributes of:
- the modeler layer
- the customization layer
- the applicative extension layer.
No mask is defined on the upper layers.
A security mask on modeller metadata is useful:
- for modeller entities that are not customizable (not CAA_Derivable and not Abstract in metadata) but that may be extensible or not
- for any extensions of such non-customizable modeller entities, since a security mask defined on an extension only concerns the attributes of this extension and not the attributes of the extended modeller entity; hence to display the views for an extension, the combination of the two masks is necessary
- for modeller entities that are "usable" types (as compared to "authoring" types) in a given environment, via the operations READ, QUERY, and EZQUERY (operations CREATE and WRITE are meaningful only for the authoring types of a given environment, i.e. customized entities in general)
- for any customized entities, since it is possible to incorporate the mask defined on the inherited modeller attributes when using the VPLMPosMaskGenerator mask file generator tool.
A security mask on a customized metadata is required since there is no mask inheritance at runtime: each entity must define its attributes (it’s own attributes plus inherited attributes) and how they are displayed in the various predefined views (Create, EZQuery, Query, Read, Write and Tree).
A sample of a customized entity is delivered, PLMProductDS, in the PLMProductDS.metadata file. The sample illustrates the principle that you can define customized entities derived from any Dassault Systèmes-defined modeller entities. An applicative extension of entity VPMReference is used for completeness.