Overview of FCS Processing | ||
| ||
Processing File Checkin and Checkout
When a user checks in or checks out a file, FCS first determines the preferred site (see The Preferred Site). Then FCS sends encrypted tickets and receipts between the FCS and MCS to send meta data and accomplish the file checkin/checkout.
The following diagram illustrates a typical configuration with a single
ENOVIA Live Collaboration Server or Main Collaboration Server (MCS) and
one or more FCSs. 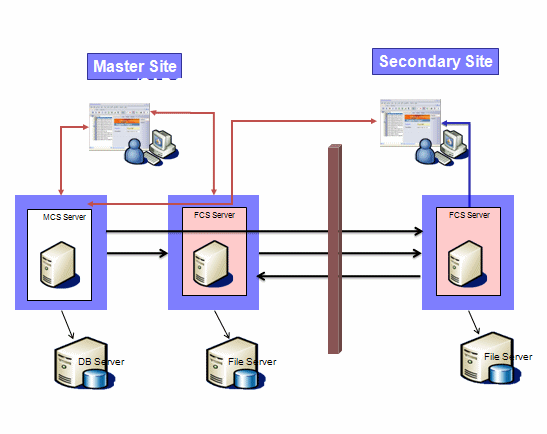
The following table explains a typical file checkin process.
| FCS Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Client/Browser | The client browser requests a file storage operation.
If the FCS is configured on this LAN, then the FCS intercepts the request
and processes it based on the ticket passed by the client. The FCS supports: Browser-based and HTTP clients. |
| File Protocol | The system uses HTTP/S for the checkin request
and all encrypted ticket/receipt transfers. The FCS checks in and checks
out files from the store or location. The FCS uses HTTP/S to get the store/location information from the ENOVIA Live Collaboration Server. The ENOVIA Live Collaboration Server communicates with the database over a LAN connection. The connection to the database, via a WAN connection, is eliminated. |
| MCS | Systems are typically configured for a single MCS and one or more FCSs servicing the local requests. |
| Tickets and Receipts | Tickets and receipts are the vehicle for moving information between the ENOVIA Live Collaboration Server and the FCS. They provide added security. |
| Triggers | The FCS uses triggers with Java Programming
Objects (JPOs) during checkin and checkout operations. Supported triggers
include: Check--Fires before an event Action--Fires after an event When a trigger fails, the system rolls back the transaction. The Override trigger type is not supported by the FCS. |
A file checkout transaction operates in a similar way, with the MCS creating the checkout job ticket, which the client machine forwards to the FCS. The FCS then copies the file to the client and returns a receipt that is sent back to the MCS. Settings in web.xml allow you to control how long a ticket or receipt is valid and how many tickets or receipts are kept before deleted.
![]()
File Transfer Protocol HTTP/S
ENOVIA Live Collaboration uses HTTP/S to transfer files between FCS locations and stores. This includes all communications between the MCS and FCS. For example, FCS uses HTTP/S to retrieve the store/location information from the MCS. The MCS communicates with the database via OCI over a LAN connection. The OCI connection to the database via a WAN connection used by the standard FCS is eliminated.
FTP is not required and should not be used for WAN transfer. FTP should be used only for local machine transfer. If an FCS location or store is configured with the FTP protocol, FTP will only be used locally for the FCS server to talk to its own FTP server. All communication between the MCS and the FCS must be via HTTP.