Replication | ||
| ||
About Replication
Sites and locations enhance checkin, checkout, and open for view or edit performance for clients that require WAN access to a centralized storage location. The central store (default) is mirrored to one or more remote machines (locations). In this way, a client at the remote site has LAN access to the data.
When a user performs a file checkin, the system writes the file to
that user's preferred location. If the preferred location is not specified, the system writes the
file to the store's default path. In the schema, the business object
is marked as having a file checked in at this location. When another
user requests the file for checkout, the system attempts the checkout
from these locations in this order:
- Locations that are part of the checkout person's preferred site. If none of these locations contain the newest copy, then:
- The store's default location. If this does not contain the newest copy, then:
- Any location that contains a valid copy of the file. This means that the system performs a sync-on-demand: the system copies the requested file to the user's preferred location and then performs the local file checkout.
For example, if you are in the United States and you have an office in Boston, and another in Paris, you could have two FCSs: one in both offices. If replication is used, it does not matter where the checkout occurs because the FCS ensures that both locations are synched up and ensures that duplicates are removed.
A user can only have one site. A site can have one or more locations. A functional store contains one or more locations. For example, suppose that:
- The user is located in Boston, so Site = Boston.
- There are 2 possible Locations: Boston and Paris.
- There are 3 possible functional Stores: Marketing, Sales, and Engineering.
For example, if the user in the example is an engineer who works in Boston, the Site would be Boston, the Store could be Engineering, and the Location could be Paris or Boston. To switch the default location, use the locationOverride switch.
When the system needs to replicate multiple files, the process is streamlined by replicating files in a single batch rather than one at a time. The system determines the list of files to be replicated and then groups them by "destination location." Files in the list can have different destination locations as long as they all have the same FCS URL, since the FCS URL for the first group of files is used for the checkout ticket. The system then replicates each group of files to the destination location in a single batch, and commits the metadata. If a replication process fails, subsequent items will not be committed but all previously committed items will remain present in the database.
A checkout operation with replication looks like this:
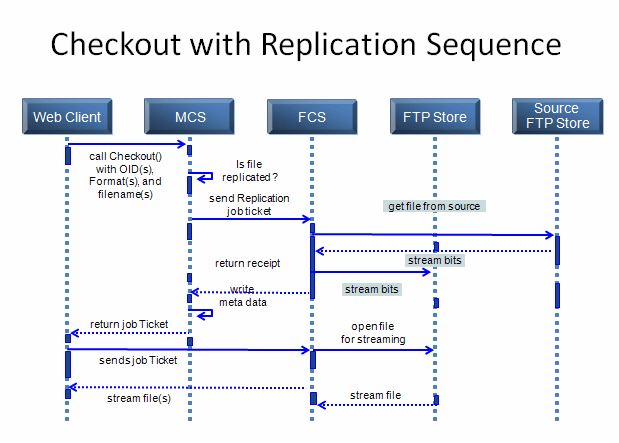
If a transaction fails, the ENOVIA Live Collaboration Server goes back and deletes the files on the remote server. If there are duplicates, the ENOVIA Live Collaboration Server deletes the duplicates that are on the FTP server that is logically part of the FCS server.
If there is more than one FCS server, the ENOVIA Live Collaboration Server cleans up the copy of the file where it was last checked in. All other copies are marked obsolete. In addition, you can write a cron job to do the tidystore cleanup operation.
![]()
Replication from a Specific Source and Destination Location
With FCS file replication, the source location is the first location that has the current file. The destination location is the requesting client's preferred location. However, you can execute a custom replication program to override this default behavior. This program must be defined on the store; then any location involved in replication with this store will use this program. Defining a program on a store allows for greater control over when the program is executed. The custom program must implement the following Java interface:
Package com.matrixone.fcs.mcs;
public interface ReplicationTrigger {
/**
* Called prior to replication.
* @param cntx
* @param inList - list of @see {@link BusinessObjectProxy}
that represent the source for file that need replication
* @param copyList - list of @see {@link
BusinessObjectProxy} that represent the destination for file
that need replication
* @return replacement inList, can be the original inList
* @throws Exception
*/
public ArrayList check(Context cntx,
ArrayList inList,
ArrayList copyList) throws Exception;
}
To define the custom replication program on the store, execute the following in MQL:
Note: The MX_FCS_REPLICATE_PROGRAM_NAME global variable should no longer be used. This program operates on one file at a time and is no longer needed now that files are replicated in a single batch. If you are currently using this program, you must replace it with the custom replication program described above. The system will now issue a warning if this legacy program is sill in use.