Editing a Metric | |||
| |||
Click
 for the metric. This icon is only available for the Goal metric and the last metric added when the Quality object is in the Initiated state.
for the metric. This icon is only available for the Goal metric and the last metric added when the Quality object is in the Initiated state.
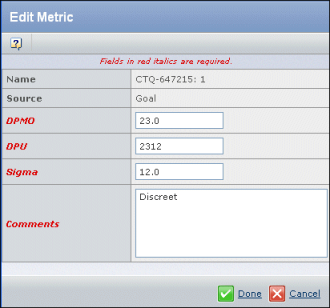
The fields listed depend on the CTQ's data type (discrete or continuous).
Choose the Source.
The Source for the Goal metric cannot be changed. Each Source can only be used once so only the unused sources are listed in the drop-down list. If you change a source to Controlled, then the Quality object is also promoted to Controlled. See Quality Metrics and Their Sources for details.
Edit the metric fields as needed.
If this is a Goal metric, enter the desired values for the end of the project. If this is any other metric source (Predicted, Allocated, Measured, Controlled), enter the predicted/actual values.
For discrete data, enter values for the following fields. All these fields allow numbers with decimals except DPU, which allows whole numbers only.
- DPMO. Defects Per Million Opportunities. The average number of defects per unit observed during an average production run divided by the number of opportunities to make a defect on the product under study during that run normalized to one million.
- DPU. Defects Per Unit is the average number of defects observed when sampling a population. DPU = Total # of Defects / Total population
- Sigma. NORMSINV(1-((Total Defects) / (Total Opportunities))) + 1.5
For continuous data, enter values for the following fields. All these fields allow numbers with decimals.
- Mean. The mean is the average data point value within a data set. To calculate the mean, add all of the individual data points then divide that figure by the total number of data points.
- Standard Deviation. Standard deviation is a statistic used to measure the variation in a distribution. Sample standard deviation is equal to the square root of (the sum of the squared deviations of the mean divided by the sample size minus 1).
- Upper Spec Limit. The upper specification limit, as specified by the customer (internal or external).
- Lower Spec Limit. The lower specification limit, as specified by the customer.
- Sigma. NORMSINV(1-((Total Defects) / (Total Opportunities))) + 1.5
Enter any Comments.
Click Done.