Click the Inactive Parts tab.
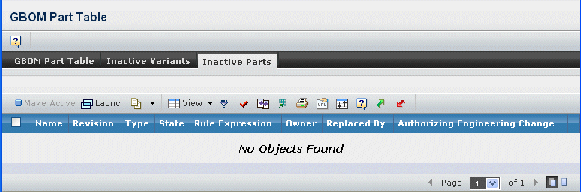
The table contains the following columns:
Name. Name of the part. This column contains highlighted links. Click on any name to view the default page for that object, or click  in the row to view the default page in a new browser window.
in the row to view the default page in a new browser window.
Revision. The revision number or code.
Type. The type or subtype.
State. The current state of the part in its lifecycle.
Rule Expression. The inclusion rule for the part before the part was made inactive. This column contains highlighted links. Click on the link and the inclusion rule expression viewer opens and is read only.
Owner. The owner of the part.
Replaced By. The part that replaced the part for a feature in the Release state. When a part is replaced, it’s moved to the inactive parts table. The Update Released Feature property must enabled to replace parts for features in the Release state. See Configuring the Properties File for more information.
Authorizing Engineering Change. The engineering change in the Active state that authorized the replacement of the part. When a part is replaced for a feature in the Release state, an active engineering change is required.